- Home
- Blog
Blog
On 30/09/2022
PowerApps functions
Parse text to number
Filter('Workflow Tasks'; ID = Value(txtId.Text))
Add datas (listItem)
Patch(NewVoie;Defaults(NewVoie);{Num_x00e9_rovoie:"0"&LookUp(NewVoie;ID=1).Num_x00e9_rovoie}))
Update context, and forms datas
SubmitForm(FormBeneficiaires);;ResetForm(FormBeneficiaires);; NewForm(FormBeneficiaires);; UpdateContext({showPopup:false});
If(IsBlankOrError(SubmitForm(Form1)), Set(saveStatus, "An error occured" & Form1.Error), Set(saveStatus, "Operation succeded"))
Navigate to another form
Navigate(Page_infos_enregistrements)
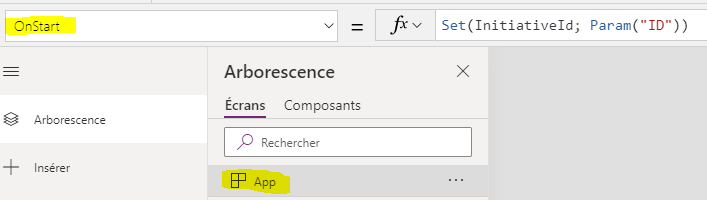
Get query string parameter and set a variable
Set(InitiativeId; Param("ID"))
Get a field from your datasource by ID
First(Filter(Initiatives; ID=1)).Nom
And Or Not
Or(And(Radio1.Selected.Value=4; !IsBlank(txtComment.Text));Radio1.Selected.Value<4)
Update Lookup Field
Patch(
ResultatAnalyses;
First(//here item to update
Filter(
ResultatAnalyses;
Affaire.Id = currentAffaire.ID And Analyse.Id = ThisItem.ID
)
);
{
Title: "notused";
Commentaires: txtGalComment.Text;
Gravite: Rating1.Value;
Affaire: {//lookup field name
Id: currentAffaire.ID;//id of lookup
Value: LookUp(
Affaires;//list who contains lookup value
ID = currentAffaire.ID;//id of lookup
currentAffaire.Title//title of lookup value
)
}
}
)
Patch Choice
TypeIntervention: {Value: dtvTypeIntervention.Selected.Value}
Execute automate with json
'My workflow'.Run(
JSON(
{
SolutionId: selectedSolution.ID,
ImageContent: UploadedImage14.Image
},
JSONFormat.IncludeBinaryData
)
);
Reg ex to get cleaned string
Clear(AttachmentsCollection);
ForAll(
RenameColumns(DataCardValue91.Attachments, "Name", "Name1"),
Collect(
AttachmentsCollection,
Name1
)
);Set(Title1, First(AttachmentsCollection).Value);Set(FileName1, Concat( Split(First(AttachmentsCollection).Value, "" ), If( IsMatch(Result, "([^A-Za-z0-9\.\-])" ), "",Result ) ))
Save Form
SubmitForm(Form1);;If(!IsBlankOrError( Form1.Error); Notify("Une erreur est survenue lors de la sauvegarde " & Form1.Error; NotificationType.Error);Notify("La savegarde a réussi";NotificationType.Information);;Set(currentElement; Form1.LastSubmit))
Sort columns
Set(Month, Distinct(SortByColumns(CurrentMonthMails, "Year", Ascending, "Month", Ascending), Month))
Set date
Set(StartDate, DateAdd(DateTimeValue( Day(Today) &"/"& Month(Today) &"/"& Year(Today) &" 00:00:00"), -30));
Sum
Sum(Filter(CurrentMonthMails, Month = ThisItem.Result ), uniqMails)
Pnp PowerShell Export Import Site
On 02/07/2025
Define JSON configuration https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/solution-guidance/configuring-the-pnp-provisioning-engine
Connect-PnPOnline -Url $siteUrl -ClientId $clientId -Tenant $tenantName -Thumbprint $cert
$xml = Get-PnPSiteTemplate -Out $SchmaXMLPath -Configuration $configPath
# Invoke-PnPSiteTemplate -Path $SchmaXMLPath
{
"$schema": "https://aka.ms/sppnp-extract-configuration-schema",
"handlers": [
"ContentTypes",
"Fields",
"Lists"
],
"persistAssetFiles": false,
"lists": {
"lists": [
{
"title": "Eutelsat Entity",
"includeItems": false,
"query": {
"includeAttachments": false
}
}
]
},
"contentTypes": {
"groups": [
"Market Access"
]
}
}
# remove particular nodes
$SchmaXMLPathDest = "MA_pmsatEntity_15.xml"
[xml]$xmlContent = Get-Content $SchmaXMLPath
Clear-Host
# Define the namespace if needed (common in SharePoint XML)
$nsmgr = New-Object System.Xml.XmlNamespaceManager($xmlContent.NameTable)
# Add the namespace you are using in the XML document. Use "ns" as a prefix here.
$nsmgr.AddNamespace("pnp", "http://schemas.dev.office.com/PnP/2022/09/ProvisioningSchema")
# Use XPath to select fields. Adjust the XPath query based on your XML structure.
$fields = $xmlContent.SelectNodes("//Field", $nsmgr)
Write-Host "cout $($fields.Count)"
# Iterate over fields and remove those whose InternalName starts with an underscore
for ($i = $fields.Count - 1; $i -ge 0; $i--) {
$internalName = $fields[$i].Attributes["Name"].Value
if ($internalName -like "_*") {
# Remove the field from its parent node
$fields[$i].ParentNode.RemoveChild($fields[$i]) | Out-Null
continue;
}
$internalName = $fields[$i].Attributes["Group"].Value
if ($internalName -eq "_Hidden") {
# Remove the field from its parent node
$fields[$i].ParentNode.RemoveChild($fields[$i]) | Out-Null
}
}
$fields = $xmlContent.SelectNodes("//pnp:ContentType", $nsmgr)
for ($i = $fields.Count - 1; $i -ge 0; $i--) {
$internalName = $fields[$i].Attributes["Name"].Value
if ($internalName -ne "MA_EutelsatEntity") {
# Remove the field from its parent node
$fields[$i].ParentNode.RemoveChild($fields[$i]) | Out-Null
}
}
# Save the modified XML back to a file
$xmlContent.Save("{0}\template\test2.xml" -f (get-location))
Sharepoint Rest Get User ID By Mail
On 23/06/2025
async function GetDigestValue(siteUrl) {//
const fetchOptions = {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json;odata=verbose',
'Content-type': 'application/json;odata=verbose'
}
};
const response = await fetch(siteUrl + "/_api/contextinfo", fetchOptions);
return (await response.json()).d.GetContextWebInformation.FormDigestValue;
}
async function EnsureUser(siteUrl, userEmail) {
const digest = await GetDigestValue(siteUrl);
console.log("digest", digest);
const body = {
'logonName': `i:0#.f|membership|${userEmail}`
}
const response = await fetch(`${siteUrl}/_api/web/ensureuser?$select=Id`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Accept": "application/json;odata=verbose",
"Content-Type": "application/json;odata=verbose",
"X-RequestDigest": digest
},
body: JSON.stringify({
'logonName': `i:0#.f|membership|${userEmail}`
})
});
console.log("response", response);
const userData = await response.json();
return userData.d.Id;
}
async function getUserIdByEmail(siteUrl, userEmail) {
try {
const fetchOptions = {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json;odata=verbose',
'Content-type': 'application/json;odata=verbose'
}
};
const response = await fetch(siteUrl + `/_api/web/siteusers/getbyemail('${encodeURIComponent(userEmail)}')`, fetchOptions);
const data = await response.json();
console.log("getUserByEmail data", data);
return data.d.Id;
} catch (error) {
console.log("getUserByEmail Error", error);
return null;
}
}
let siteUrl1 = "https://eutelsatgroup.sharepoint.com/sites/fdiSandBox";
let email1 = "ffdietrich-ext@eutelsat.com";
let ret = await EnsureUser(siteUrl1, email1);
console.log("response", ret);
const siteUrl = "https://test.sharepoint.com/sites/Dev_wf";
const email = "fpalmo@test.com";
console.log("response", ret0);
const ret = await EnsureUser(siteUrl, email);
const ret0 = await getUserIdByEmail(siteUrl, email);
console.log("response", ret);
On 27/05/2025
// Fonction pour récupérer tous les RoleDefinitionBindings
async function getRoleDefinitionBindings(list, Id, Title, ServerRelativeUrl, ItemsCount, Hidden, HasUniqueRoleAssignments) {
let p = `vdfvd`;//$${apiGet}
const getPai = `${list}/roleassignments?$expand=Member/users,RoleDefinitionBindings`;
console.log("request", getPai);
const response = await fetch(getPai, {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json;odata=verbose'
}
});
const data = await response.json();
data.d.results;
console.log(data.d.results);
const ret = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.d.results.length; i++) {
var perm = data.d.results[i];
const toAdd = {};
toAdd.ListId = Id;
toAdd.ListTitle = Title;
toAdd.ListServerRelativeUrl = ServerRelativeUrl;
toAdd.ItemsCount = ItemsCount;
toAdd.Hidden = Hidden;
toAdd.HasUniqueRoleAssignments = HasUniqueRoleAssignments;
toAdd.Id = perm.Member.Id;
toAdd.LoginName = perm.Member.LoginName;
toAdd.Email = perm.Member.Email ?? "";
toAdd.Description = perm.Member.Description;
toAdd.Title = perm.Member.Title;
toAdd.IsHiddenInUI = perm.Member.IsHiddenInUI;
toAdd.PrincipalId = perm.Member.PrincipalId;
toAdd.PrincipalType = perm.Member.PrincipalType;
//users bu group
if (perm.Member.Users !== undefined && perm.Member.Users !== null && perm.Member.Users.results.length > 0) {
toAdd.Users = [];
for (let j = 0; j < perm.Member.Users.results.length; j++) {
const u = perm.Member.Users.results[j];
toAdd.Users.push({
Email: u.Email,
Id: u.Id,
Title: u.Title,
UserPrincipalName: u.UserPrincipalName,
IsSiteAdmin: u.IsSiteAdmin,
IsShareByEmailGuestUser: u.IsShareByEmailGuestUser
});
}
}
toAdd.RoleDefinitionBindings = ""
if (perm.RoleDefinitionBindings !== undefined && perm.RoleDefinitionBindings !== null && perm.RoleDefinitionBindings.results.length > 0) {
for (let j = 0; j < 1; j++) {
const r = perm.RoleDefinitionBindings.results[j];
toAdd.RoleDefinitionBindings = r.Name;
}
}
ret.push(toAdd);
}
console.log(ret);
return ret;
}
let url = "https://test.sharepoint.com/sites/csc";
let lists = `${url}/_api/web/lists?$select=Hidden,Title,RootFolder/ServerRelativeUrl,Id,ItemCount,HasUniqueRoleAssignments&$expand=RootFolder`;//&$filter=Hidden eq false
let response = await fetch(lists, {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json;odata=verbose'
}
});
let data = await response.json();
let datas = [];
for (let z = 0; z < data.d.results.length; z++) {//
const lst = data.d.results[z];
console.log("lst", lst);
const datas1 = await getRoleDefinitionBindings(`${url}/_api/web/lists(guid'${lst.Id}')`, lst.Id, lst.Title, lst.RootFolder.ServerRelativeUrl, lst.ItemCount, lst.Hidden, lst.HasUniqueRoleAssignments);
console.log(datas1);
for (let u = 0; u < datas1.length; u++) {
datas.push(datas1[u]);
}
}
console.log("datas", datas);
let csv = "ListId;ListTitle;ListServerRelativeUrl;ItemsCount;Hidden;HasUniqueRoleAssignments;MemberTitle;MemberEmail;MemberLoginName;MemberId;MemberDescription;Permission;TopLevel;UserMail;UserTitle;UserId;UserUserPrincipalName;IsSiteAdmin;IsShareByEmailGuestUser\n";
for (let k = 0; k < datas.length; k++) {
const d = datas[k];
let member = "";
member += `${d.ListId};`
member += `${d.ListTitle};`
member += `${d.ListServerRelativeUrl};`
member += `${d.ItemsCount};`
member += `${d.Hidden};`
member += `${d.HasUniqueRoleAssignments};`
member += `${d.Title};`
member += `${d.Email};`
member += `${d.LoginName};`
member += `${d.Id};`
member += `${d.Description ?? ""};`
member += `${d.RoleDefinitionBindings};`
csv += `${member}true;;;;;;\n`;
//debugger;
if (d.Users !== undefined) {
for (let j = 0; j < d.Users.length; j++) {
const user = d.Users[j];
let u = `${member}false;`;
u += `${user.Email};`;
u += `${user.Title};`;
u += `${user.Id};`;
u += `${user.UserPrincipalName ?? ""};`;
u += `${user.IsSiteAdmin};`;
u += `${user.IsShareByEmailGuestUser}`;
csv += `${u}\n`
}
}
}
console.log(csv);
On 27/05/2025
// Fonction pour récupérer tous les RoleDefinitionBindings
async function getRoleDefinitionBindings(apiGet, type) {
let p = `vdfvd`;//$${apiGet}
const getPai = `${apiGet}/roleassignments?$expand=Member/users,RoleDefinitionBindings`;
const response = await fetch(getPai, {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json;odata=verbose'
}
});
const data = await response.json();
data.d.results;
console.log(data.d.results);
const ret = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.d.results.length; i++) {
var perm = data.d.results[i];
const toAdd = {};
toAdd.type = type;
toAdd.Id = perm.Member.Id;
toAdd.LoginName = perm.Member.LoginName;
toAdd.Email = perm.Member.Email ?? "";
toAdd.Description = perm.Member.Description;
toAdd.Title = perm.Member.Title;
toAdd.IsHiddenInUI = perm.Member.IsHiddenInUI;
toAdd.PrincipalId = perm.Member.PrincipalId;
toAdd.PrincipalType = perm.Member.PrincipalType;
//users bu group
if (perm.Member.Users !== undefined && perm.Member.Users !== null && perm.Member.Users.results.length > 0) {
toAdd.Users = [];
for (let j = 0; j < perm.Member.Users.results.length; j++) {
const u = perm.Member.Users.results[j];
toAdd.Users.push({
Email: u.Email,
Id: u.Id,
Title: u.Title,
UserPrincipalName: u.UserPrincipalName,
IsSiteAdmin: u.IsSiteAdmin,
IsShareByEmailGuestUser: u.IsShareByEmailGuestUser
});
}
}
//debugger;
// = [];
toAdd.RoleDefinitionBindings = ""
if (perm.RoleDefinitionBindings !== undefined && perm.RoleDefinitionBindings !== null && perm.RoleDefinitionBindings.results.length > 0) {
for (let j = 0; j < 1; j++) {
const r = perm.RoleDefinitionBindings.results[j];
toAdd.RoleDefinitionBindings = r.Name;
// toAdd.RoleDefinitionBindings = {
// Name: r.Name,
// Hidden: r.Hidden,
// Description: r.Description,
// RoleTypeKind: r.RoleTypeKind,
// Order: r.Order
// };
}
}
ret.push(toAdd);
}
console.dir("ret", ret);
console.log(ret);
return ret;
}
let url = "https://test.sharepoint.com/sites/csc";
debugger;
const datas = await getRoleDefinitionBindings(`${url}/_api/web`, "SiteCollection");
let csv = "type;MemberTitle;MemberEmail;MemberLoginName;MemberId;MemberDescription;Permission;TopLevel;UserMail;UserTitle;UserId;UserUserPrincipalName;IsSiteAdmin;IsShareByEmailGuestUser\n";
for (let k = 0; k < datas.length; k++) {
const d = datas[k];
let member = "";
member += `${d.type};`
member += `${d.Title};`
member += `${d.Email};`
member += `${d.LoginName};`
member += `${d.Id};`
member += `${d.Description ?? ""};`
member += `${d.RoleDefinitionBindings};`
csv += `${member}true;;;;;;\n`;
//debugger;
if (d.Users !== undefined) {
for (let j = 0; j < d.Users.length; j++) {
const user = d.Users[j];
let u = `${member}false;`;
u += `${user.Email};`;
u += `${user.Title};`;
u += `${user.Id};`;
u += `${user.UserPrincipalName ?? ""};`;
u += `${user.IsSiteAdmin};`;
u += `${user.IsShareByEmailGuestUser}`;
csv += `${u}\n`
}
}
}
console.log(csv);
PowerShell Compaire Property Items
On 26/05/2025
$ret1 = "PO-REQ-..2101.docx" # $ret2 = "PO-RE..-2101.pdf" $url1 = "https://test.sharepoint.com/sites/test/procedures"; $url2 = "https://test.sharepoint.com/sites/test/procedures" Clear-Host function ToPdf { param($fileName) $paths = $fileName.Split(".") if ($paths.Count -eq 2) { return "$($paths[0]).pdf" } if ($paths.Count -gt 2) { $ret = ""; for ($i = 0 ; $i -lt $paths.Count - 1 ; $i++) { $ret += "$($paths[$i])" + "." } $ret += "pdf" return $ret } throw "Error : $($fileName)" } $list = "Work Instructions - Sources" $list2 = "Work Instructions" $ColumnsToCompaire = "Csc_Domain" $ColumnRef = "" $select = "Title,FileLeafRef,Csc_Domain,FileDirRef" $buildSelet = "<View Scope='RecursiveAll'><RowLimit>1000</RowLimit><OrderBy><FieldRef Name='Modified' Ascending='FALSE' /></OrderBy><Query><Where><Neq><FieldRef Name='FSObjType' /><Value Type='Integer'>1</Value></Neq></Where></Query>$($select)</View>" foreach ($col in ($select -split ",")) { $buildSelet += " " $con1 = Connect-PnPOnline -Url $url1 -ReturnConnection -UseWebLogin $con2 = Connect-PnPOnline -Url $url2 -ReturnConnection -UseWebLogin $list1 = Get-PnPList -Identity $list -Connection $con1 Write-Host "list 1 : $($list1.ItemCount)" $query = "" } $buildSelet += " " $items1 = Get-PnPListItem -List $list -Connection $con1 -Query $query $items2 = Get-PnPListItem -List $list2 -Connection $con2 -Query $query foreach ($item in $items1) { if ("$($item[$ColumnsToCompaire] )".Trim().ToLower() -eq "") { continue; } Write-Host "" Write-Host "list 1 : $($list1.ItemCount) item $($item.Id) ------------------" foreach ($col in ($select -split ",")) { Write-Host "item $($item.Id) '$($col)' : '$($item[$col])'" "item 1 $($item.Id) '$($col)' : '$($item[$col])'" | Out-File -LiteralPath ".\log\myLog_1.txt" -Encoding utf8 -Append } #$found = $items2 | Where-Object {$_.FileLeafRef -eq $item["FileLeafRef"]} #) -and $_.FileDirRef -eq $item["FileDirRef"] $founds = @(); $toFound = ToPdf -fileName $item["FileLeafRef"] foreach ($found in $items2) { if ("$($toFound)".Trim().ToLower() -eq "$($found["FileLeafRef"])".Trim().ToLower()) { $founds += $found } } if ($null -eq $founds) { Write-Error "File Error : $($item["FileLeafRef"]))" -ForegroundColor Yellow } elseif ($founds.Count -eq 0) { Write-Host "File ne found $($($item["FileLeafRef"])) -> $($toFound)" -ForegroundColor Yellow "File ne found $($($item["FileLeafRef"])) -> $($toFound)" | Out-File -LiteralPath ".\log\myLog_NotFound.txt" -Encoding utf8 -Append } elseif ($founds.Count -gt 1) { Write-Error "More than 1 file" } elseif ($founds.Count -eq 1) { if ($item[$ColumnsToCompaire] -ne $founds[0][$ColumnsToCompaire]) { Write-Host "to update" "to update $($item.Id) '$($toFound)' - origine : '$($item[$ColumnsToCompaire])' - pdf : '$($founds[0][$ColumnsToCompaire])'" | Out-File -LiteralPath ".\log\myLog_2.txt" -Encoding utf8 -Append Set-PnPListItem -UpdateType SystemUpdate -Identity $founds[0].Id -Connection $con2 -List $list2 -Values @{$ColumnsToCompaire = $item[$ColumnsToCompaire] } Write-Host "updated" } } }
On 01/04/2025
<html>
<head>
<style>
.button {
background-color: white;
border: none;
Border-radius:5px;
color: black;
padding: 15px 32px;
border: 2px solid #008CBA;
text-align: center;
font-weight : bold ;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
margin: 4px 2px;
cursor: pointer;
top: 38%;
right: 27%;
position:absolute;
}
.button:hover {
background-color: #008CBA;
color: white;
}
.imagestyle{
width: 50%;
margin-left: 20%;
position: absolute;
top: -105px;
display:none;
}
@media print {
@page {
size:auto;
margin:.5rem 0;
}
#printPageButton {
display: none;
}
#imagestyleId{
display:block;
}
[data-automation-id^=QuickLinksWebPart]{
display: none !important;
}
[data-automation-id=TitleTextId]{
padding-top: 100px;
}
[data-automation-id=CanvasSection]{
top: -140px;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function generatePdf() {
const pageTitle = document.title;
const printTitle = 'Mandate ' + pageTitle;
document.title = printTitle;
window.print();
document.title = pageTitle;
return false;
}
</script>
<input type="button" class="button"
id="printPageButton"
value="Generate Mandate" onclick="generatePdf()">
<img src="tlstLogo.png" class="imagestyle" id="imagestyleId"/>
</body>
</html>
Sharepoint Rest Compaire 2 Lists Fields
On 25/03/2025
// Fonction pour comparer les champs de deux listes SharePoint
async function compareSharePointLists(urlSite1, urlSite2, ListRelativeUrl1, ListRelativeUrl2) {
// Fonction auxiliaire pour obtenir les champs de la liste
async function getListFields(urlSite, ListRelativeUrl) {
const response = await fetch(`${urlSite}/_api/web/lists/getbytitle('${ListRelativeUrl}')/fields?$select=InternalName,TypeAsString`, {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json;odata=verbose',
},
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`Error fetching fields for list at ${ListRelativeUrl}: ${response.statusText}`);
}
const data = await response.json();
return data.d.results;
}
try {
// Obtenir les champs des deux listes
const fields1 = await getListFields(urlSite1, ListRelativeUrl1);
const fields2 = await getListFields(urlSite2, ListRelativeUrl2);
// Comparer les champs
fields1.forEach(field1 => {
const matchingField = fields2.find(field2 => field2.InternalName === field1.InternalName);
if (!matchingField) {
console.log(`Le champ ${field1.InternalName} est manquant dans ${ListRelativeUrl2} de ${urlSite2}`);
} else if (field1.TypeAsString !== matchingField.TypeAsString) {
console.log(`Le type de champ ${field1.InternalName} ne correspond pas dans ${ListRelativeUrl2} de ${urlSite2} : ${field1.TypeAsString} vs ${matchingField.TypeAsString}`);
}
});
fields2.forEach(field2 => {
const matchingField = fields1.find(field1 => field1.InternalName === field2.InternalName);
if (!matchingField) {
console.log(`Le champ ${field2.InternalName} type ${field2.TypeAsString} est manquant dans ${ListRelativeUrl1} de ${urlSite1}`);
}
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Erreur lors de la comparaison des champs des listes :', error);
}
}
// Example usage
compareSharePointLists(
'https://test.sharepoint.com/sites/DoceboMigration',
'https://test2.sharepoint.com/sites/fdiSandBox',
'testConfiguration',
'fdiTasks');
