- Home
- Blog
Blog
Sharepoint json formatting status icons
On 18/03/2025
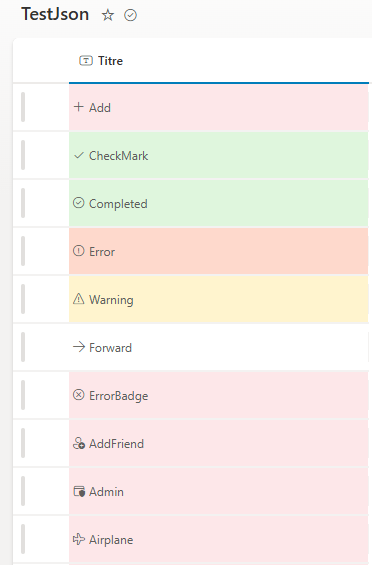
Here are the CSS classes used in JSON column formatting as sp-field-severity: sp-field-severity--low: This class is used to indicate a low severity level. It typically applies a specific style to represent low urgency or importance1234. sp-field-severity--good: This class is used to indicate a good or positive status. It applies a style that signifies a favorable condition1234. sp-field-severity--warning: This class is used to indicate a warning level. It applies a style that signifies caution or a moderate level of urgency1234. sp-field-severity--severeWarning: This class is used to indicate a severe warning level. It applies a style that signifies a high level of urgency or importance12354. sp-field-severity--blocked: This class is used to indicate a blocked or critical status. It applies a style that signifies a very high level of urgency or a critical issue12354. These classes are part of the SharePoint framework and are used to apply consistent styling across different columns based on the severity or status of the data. { "$schema": "https://developer.microsoft.com/json-schemas/sp/v2/column-formatting.schema.json", "elmType": "div", "attributes": { "class": "=if(@currentField == 'CheckMark', 'sp-field-severity--good', if(@currentField == 'Completed', 'sp-field-severity--good', if(@currentField == 'Forward', 'sp-field-severity--low', if(@currentField == 'Warning', 'sp-field-severity--warning', if(@currentField == 'Error', 'sp-field-severity--severeWarning', if(@currentField == 'ErrorBadge', 'sp-field-severity--blocked', '')))))) + ' ms-fontColor-neutralSecondary'" }, "children": [ { "elmType": "span", "style": { "display": "inline-block", "padding": "0 4px" }, "attributes": { "iconName": "@currentField" } }, { "elmType": "span", "txtContent": "@currentField" } ] } CheckMark Completed Error Warning Forward ErrorBadge Add AddFriend Admin Airplane Alert AlignCenter AlignLeft AlignRight Archive ArrowDown ArrowLeft ArrowRight ArrowUp Attach Back Blocked Bold Bookmark Calendar Camera Cancel Checkbox CheckboxComposite CheckboxIndeterminate Checkmark ChevronDown ChevronLeft ChevronRight ChevronUp CircleRing Clear Clock Close Cloud Code CollapseMenu Color Comment Contact Copy CreditCard DataUsage Delete Dismiss Document Edit Education Emoji Error ErrorBadge Event Favorite Filter Flag Folder Forward Gift Globe Group Help History Home Important Info Italic Link List Location Lock Mail Map Megaphone Mention Message More Music NavigateBack NavigateForward News Note Open Paste Pause People Phone Photo Pin Play Print Product Redo Refresh Remove Reply Save Search Send Settings Share Shop ShoppingCart SignOut Sort Star Status Story Tag Task Trash Undo Unlock Upload User Video View Warning Work
PowerShell SharePoint Search Extract File Content
On 12/03/2025
# Parameters
$siteUrl = "https://xxxx.sharepoint.com/sites/xxxx"
$outputFilePath = "report4.txt"
$doclibpath = "/Connectivity"
# Connect to the SharePoint site
Connect-PnPOnline -Url $siteUrl -UseWebLogin
# Initialize the output file
if (Test-Path $outputFilePath) {
Remove-Item $outputFilePath
}
New-Item -Path $outputFilePath -ItemType File
# Define the search query to find '.url' files
$query = "Path:$($siteUrl)* And FileExtension:url"
$query = "Path:$($siteUrl)$($doclibpath)* And *.url"
# Execute the search query
$searchResults = Submit-PnPSearchQuery -Query $query -ErrorAction Stop -All -TrimDuplicates $true -SelectProperties "Path,FileName"
Write-Host "nb files found $($searchResults.TotalRows)"
# Check if there are any search results
if ($null -eq $searchResults -or $searchResults.TotalRows -eq 0) {
Write-Host "No '.url' files found in the search results."
Exit
}
# Initialize a variable to store combined content
$combinedContent = ""
$count = 0;
# Iterate through each search result
foreach ($result in $searchResults.ResultRows) {# ResultRows PrimarySearchResults
# Get the file URL
$fileUrl = $result.Path
if(-not $result.Path.ToLower().EndsWith(".url")){
continue;
}
$count++;
# Get the file content
$fileContent = $null;
# $fileContent = Get-PnPFileContent -Url $fileUrl -AsString -ErrorAction Stop
try {
$fileContent = Get-PnPFile -Url $fileUrl.Replace("https://eutelsatgroup.sharepoint.com", "") -AsString
}
catch {
Write-Host "File '$($fileUrl)' error. $($_)"
continue;
}
#$fileContent = Get-PnPFile -Url $fileUrl -AsString
# Check if the file content is null or empty
if ([string]::IsNullOrEmpty($fileContent)) {
Write-Host "File '$fileUrl' is empty or null."
continue
}
# Append the file content to the combined content
$combinedContent += $result.FileName + "`n"
$combinedContent += $fileUrl + "`n"
$combinedContent += $fileContent + "`n`n"
}
# Write the combined content to the output file
Add-Content -Path $outputFilePath -Value $combinedContent
# Disconnect from SharePoint Online
Disconnect-PnPOnline
Write-Host "nb files treated: $($count) Combined content written to '$($outputFilePath)'."
On 25/02/2025
Fluent UI Components and Properties
Button
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| text | The text to display on the button. |
| iconProps | Properties to pass to the icon. |
| onClick | Callback for when the button is clicked. |
| disabled | Whether the button is disabled. |
TextField
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| label | The label for the text field. |
| value | The value of the text field. |
| onChange | Callback for when the value changes. |
| placeholder | Placeholder text for the text field. |
| disabled | Whether the text field is disabled. |
Dropdown
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| label | The label for the dropdown. |
| options | Array of options to display in the dropdown. |
| selectedKey | The key of the selected option. |
| onChange | Callback for when the selected option changes. |
| placeholder | Placeholder text for the dropdown. |
| disabled | Whether the dropdown is disabled. |
Checkbox
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| label | The label for the checkbox. |
| checked | Whether the checkbox is checked. |
| onChange | Callback for when the checkbox is toggled. |
| disabled | Whether the checkbox is disabled. |
Toggle
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| label | The label for the toggle. |
| checked | Whether the toggle is checked. |
| onChange | Callback for when the toggle is toggled. |
| disabled | Whether the toggle is disabled. |
Modal
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| isOpen | Whether the modal is open. |
| onDismiss | Callback for when the modal is dismissed. |
| isBlocking | Whether the modal is blocking. |
| containerClassName | Custom class name for the modal container. |
Panel
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| isOpen | Whether the panel is open. |
| onDismiss | Callback for when the panel is dismissed. |
| headerText | The text to display in the panel header. |
| closeButtonAriaLabel | The ARIA label for the close button. |
DetailsList
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| items | Array of items to display in the list. |
| columns | Array of column definitions. |
| onItemInvoked | Callback for when an item is invoked. |
| selection | Selection object to manage selected items. |
Icon
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| iconName | The name of the icon to display. |
| style | Custom styles for the icon. |
| className | Custom class name for the icon. |
Spinner
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| label | The label for the spinner. |
| size | The size of the spinner (e.g., 'small', 'medium', 'large'). |
| ariaLive | The ARIA live region attribute. |
MessageBar
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| messageBarType | The type of the message bar (e.g., 'info', 'success', 'warning', 'error'). |
| isMultiline | Whether the message bar should display multiple lines. |
| onDismiss | Callback for when the message bar is dismissed. |
| dismissButtonAriaLabel | The ARIA label for the dismiss button. |
Sharepoint List get list fields in console
On 20/02/2025
function getUrlParams() {
const params = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search);
const urlParams = {};
for (const [key, value] of params.entries()) {
urlParams[key] = value;
}
return urlParams;
}
async function getSharePointListFields(listId) {
const apiUrl = `${_spPageContextInfo.webAbsoluteUrl}/_api/web/lists(guid'${listId}')/fields?$select=InternalName&$orderby=InternalName&$filter=Hidden eq false`;
try {
const response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json;odata=verbose',
'Content-Type': 'application/json;odata=verbose',
},
credentials: 'include', // Include credentials for authenticated requests
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Network response was not ok');
}
const data = await response.json();
return data.d.results;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching SharePoint list fields:', error);
return [];
}
}
// Usage
const urlParams = getUrlParams();
const listId = urlParams.List;
window.Fields = "";
if (listId) {
getSharePointListFields(listId).then((fields) => {
console.log('SharePoint List Fields:', fields);
// Process the fields as needed
fields.map((f) => {
window.Fields += `${f.InternalName}\n`;
});
console.log(window.Fields);
});
} else {
console.error('List ID not found in URL parameters');
}
On 04/02/2025
Les RegEx de définir des motifs de recherche complexes et de les appliquer à des chaînes de texte. Voici une explication détaillée de leur fonctionnement :
1. Création d'une Expression Régulière
En JavaScript, vous pouvez créer une expression régulière de deux manières :
- Littérale : En utilisant des barres obliques `/`.
- Objet `RegExp` : En utilisant le constructeur `RegExp`.
Exemple Littéral :
javascript
let regex = /motif/;
Exemple avec `RegExp` :
javascript
let regex = new RegExp("motif");
2. Utilisation des Expressions Régulières
Les expressions régulières peuvent être utilisées avec plusieurs méthodes de chaînes de caractères et d'objets `RegExp`.
Méthodes de Chaînes de Caractères :
- `search()` : Recherche une correspondance et retourne l'index de la première occurrence.
- `match()` : Recherche toutes les correspondances et retourne un tableau des résultats.
- `replace()` : Remplace les correspondances par une autre chaîne.
- `split()` : Divise une chaîne en un tableau basé sur les correspondances.
Méthodes de l'Objet `RegExp` :
- `test()` : Vérifie si une chaîne contient une correspondance.
- `exec()` : Recherche une correspondance et retourne un tableau d'informations sur la correspondance.
3. Exemples Pratiques
Rechercher une Correspondance :
javascript
let str = "Bonjour, monde!";
let regex = /monde/;
let result = str.search(regex); // Retourne 9
Trouver Toutes les Correspondances :
javascript
let str = "Bonjour, monde! Bonjour, tout le monde!";
let regex = /Bonjour/g; // Le flag 'g' signifie global, pour trouver toutes les occurrences
let result = str.match(regex); // Retourne ["Bonjour", "Bonjour"]
Remplacer des Correspondances :
javascript
let str = "Bonjour, monde!";
let regex = /monde/;
let result = str.replace(regex, "univers"); // Retourne "Bonjour, univers!"
Diviser une Chaîne :
javascript
let str = "un,deux,trois";
let regex = /,/;
let result = str.split(regex); // Retourne ["un", "deux", "trois"]
Tester une Correspondance :
javascript
let str = "Bonjour, monde!";
let regex = /monde/;
let result = regex.test(str); // Retourne true
Utiliser `exec()` :
javascript
let str = "Bonjour, monde!";
let regex = /monde/;
let result = regex.exec(str); // Retourne ["monde", index: 9, input: "Bonjour, monde!", groups: undefined]
4. Flags (Drapeaux)
Les expressions régulières peuvent inclure des flags pour modifier leur comportement :
- `i` : Ignore la casse (case-insensitive).
- `g` : Recherche globalement (trouve toutes les occurrences).
- `m` : Mode multi-ligne (traiter chaque ligne séparément).
- `s` : Mode dotAll (le point `.` correspond aussi aux sauts de ligne).
- `u` : Mode Unicode.
- `y` : Mode sticky (recherche à partir de la position `lastIndex`).
Exemple avec Flags :
javascript
let regex = /bonjour/i; // Ignore la casse
let result = regex.test("Bonjour"); // Retourne true
5. Motifs de Recherche
Les expressions régulières permettent de définir des motifs complexes :
- `^` : Début de la chaîne.
- `$` : Fin de la chaîne.
- `.` : N'importe quel caractère sauf un saut de ligne.
- `\d` : Un chiffre.
- `\w` : Un caractère alphanumérique.
- `\s` : Un espace blanc.
- `*` : Zéro ou plusieurs occurrences du motif précédent.
- `+` : Une ou plusieurs occurrences du motif précédent.
- `?` : Zéro ou une occurrence du motif précédent.
- `{n}` : Exactement `n` occurrences du motif précédent.
- `{n,m}` : Entre `n` et `m` occurrences du motif précédent.
Exemple de Motif Complexe :
javascript
let regex = /^\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}$/; // Correspond à un numéro de sécurité sociale américain
let result = regex.test("123-45-6789"); // Retourne true
Conclusion
Les expressions régulières en JavaScript sont un outil puissant pour manipuler des chaînes de caractères. Elles permettent de définir des motifs de recherche complexes et de les appliquer à des chaînes de texte de manière flexible et efficace. En maîtrisant les motifs de recherche et les méthodes associées, vous pouvez accomplir des tâches de traitement de texte avancées.
Understanding Regular Expressions RegEX Javascript
On 04/02/2025
Understanding Regular Expressions (RegEX) in JavaScript
Regular expressions (RegEX) in JavaScript are a powerful tool for searching and manipulating strings. They allow you to define complex search patterns and apply them to text strings. Here is a detailed explanation of how they work:
1. Creating a Regular Expression
In JavaScript, you can create a regular expression in two ways:
- Literal: Using slashes
/. - RegExp Object: Using the
RegExpconstructor.
Literal Example:
let regex = /pattern/;
RegExp Object Example:
let regex = new RegExp("pattern");
2. Using Regular Expressions
Regular expressions can be used with several string methods and RegExp object methods.
String Methods:
search(): Searches for a match and returns the index of the first occurrence.match(): Searches for all matches and returns an array of results.replace(): Replaces matches with another string.split(): Splits a string into an array based on matches.
RegExp Object Methods:
test(): Checks if a string contains a match.exec(): Searches for a match and returns an array of information about the match.
3. Practical Examples
Search for a Match:
let str = "Hello, world!"; let regex = /world/; let result = str.search(regex); // Returns 7
Find All Matches:
let str = "Hello, world! Hello, everyone!";
let regex = /Hello/g; // The 'g' flag means global, to find all occurrences
let result = str.match(regex); // Returns ["Hello", "Hello"]
Replace Matches:
let str = "Hello, world!"; let regex = /world/; let result = str.replace(regex, "universe"); // Returns "Hello, universe!"
Split a String:
let str = "one,two,three"; let regex = /,/; let result = str.split(regex); // Returns ["one", "two", "three"]
Test for a Match:
let str = "Hello, world!"; let regex = /world/; let result = regex.test(str); // Returns true
Use exec():
let str = "Hello, world!"; let regex = /world/; let result = regex.exec(str); // Returns ["world", index: 7, input: "Hello, world!", groups: undefined]
4. Flags
Regular expressions can include flags to modify their behavior:
i: Case-insensitive.g: Global search (find all occurrences).m: Multi-line mode (treat each line separately).s: DotAll mode (the dot.matches newlines).u: Unicode mode.y: Sticky mode (search from thelastIndexposition).
Example with Flags:
let regex = /hello/i; // Case-insensitive let result = regex.test("Hello"); // Returns true
5. Search Patterns
Regular expressions allow you to define complex patterns:
^: Start of the string.$: End of the string..: Any character except a newline.\d: A digit.\w: An alphanumeric character.\s: A whitespace character.*: Zero or more occurrences of the preceding pattern.+: One or more occurrences of the preceding pattern.?: Zero or one occurrence of the preceding pattern.{n}: Exactlynoccurrences of the preceding pattern.{n,m}: Betweennandmoccurrences of the preceding pattern.
Complex Pattern Example:
let regex = /^\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}$/; // Matches a US Social Security Number
let result = regex.test("123-45-6789"); // Returns true
Conclusion
Regular expressions in JavaScript are a powerful tool for manipulating strings. They allow you to define complex search patterns and apply them to text strings flexibly and efficiently. By mastering search patterns and associated methods, you can accomplish advanced text processing tasks.
On 03/02/2025
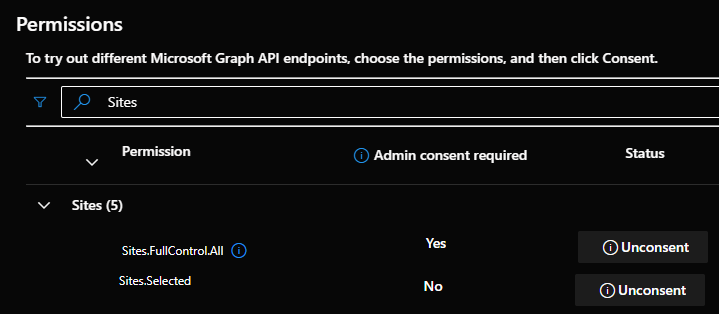
How to give permission for an Azure app you has permission : Sites.Selected
You must be admin of Azure
In Graph Explorer use this request to get the Azure Id of you Site
Add for permission Sites.selected and Site.FullControl for the account (in modify permissions Tab)
https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/sites/m365x87466739.sharepoint.com:/sites/allcompany?$select=id
replace the m365x87466739 by your Tenant name, and allcompany by the name / url of your site,
it wiil returns you the azure id of your site
{
"@odata.context": "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/$metadata#sites(id)/$entity",
"id": "m365x87466739.sharepoint.com,1dc83cb4-d304-4afa-a0ff-cf33270f1c8b,e615f00e-ac05-4dfc-928e-e51688e8273b"
}
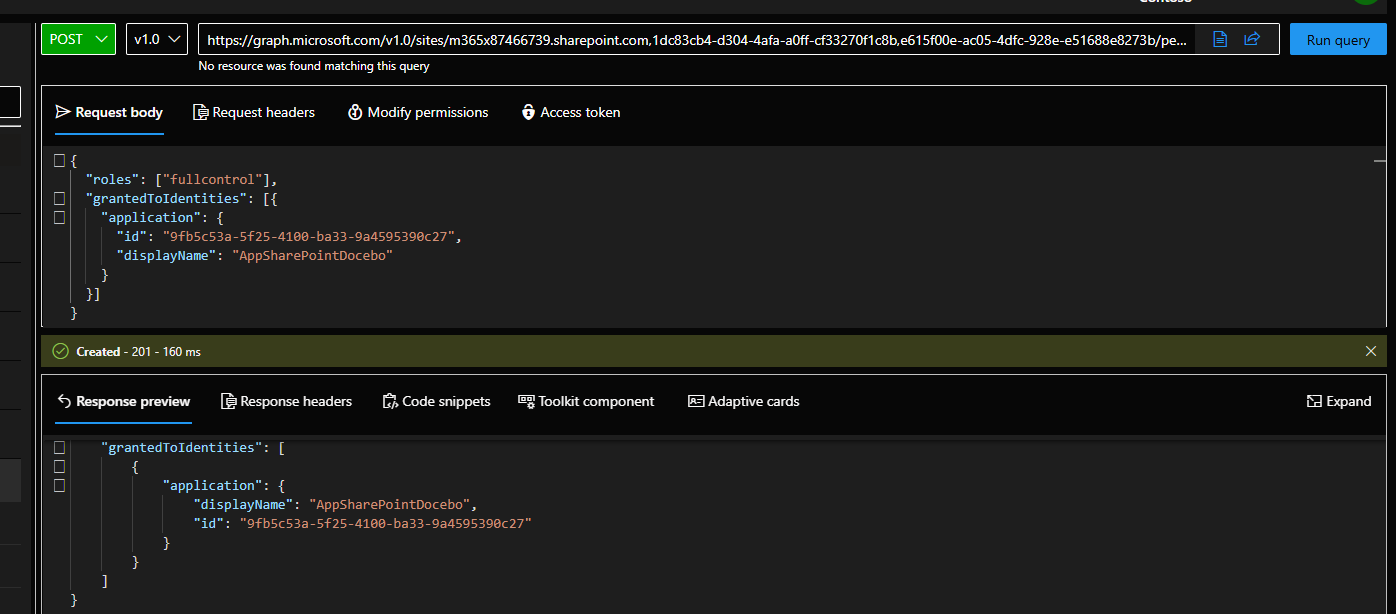
Then post a news query https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/sites/m365x87466739.sharepoint.com,1dc83cb4-d304-4afa-a0ff-cf33270f1c8b,e615f00e-ac05-4dfc-928e-e51688e8273b/permissions
{
"roles": ["write"],//permission level you want to give
"grantedToIdentities": [{
"application": {
"id": "9fb5c53a-5f25-4100-ba33-9a4595390c27",//this is you App Id
"displayName": "AppSharePointDocebo"
}
}]
}
then you can use Connect-PnPOnline -Url $siteUrl -ClientId $clientId -Thumbprint $thumbprint -Tenant $tenantId
You can use site.url /_layouts/15/appinv.aspx opage, but you must be site coll Admin, and admin SharePoint on Azure
<AppPermissionRequests AllowAppOnlyPolicy="true">
<AppPermissionRequest Scope="https://myTrenant.sharepoint.com/sites/sites/site1" Right="FullControl" />
</AppPermissionRequests>
Fileshare Migration to SharePoint
On 07/01/2025
Use SharePoint Migration Tool to upload your folder in a document library, here base settings in a json file
{
"Tasks": [
{
"SourcePath": "\\\\mySite.fr\\divisions\\Processed matrices\\Doc1",
"TargetPath": "https://test.sharepoint.com/sites/test1",
"TargetList": "FDbase",
"TargetListRelativePath": "Satellites/Doc1",
"Options": {
"PreserveFileSharePermissions": false,
"MigrateHiddenFiles": true,
"MigrateReadOnlyFiles": true,
"PreserveLastModifiedTime": true,
"PreserveCreatedTime": true,
"SkipEmptyFolders": false
}
}
]
}